Throughout history, humans have worked to improve their quality of life and to solve problems by inventing new tools. From the wheel and the steam engine to the internet and artificial intelligence (AI), each innovation has reshaped society in profound ways. Unsurprisingly, today’s businesses also understand that innovation drives growth, and they now have a new means of pushing forward: generative AI. GenAI stands as a transformative tool capable of boosting workforce productivity, streamlining operations, and enhancing customer engagement.
The democratization of GenAI has provided widespread access to powerful AI tools that once required extensive technical expertise. Yet, while GenAI offers immense benefits, it also presents challenges. This article explores how small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) can leverage GenAI to gain a competitive edge while addressing common risks and strategies to mitigate them.
GenAI: The Small Business Equalizer
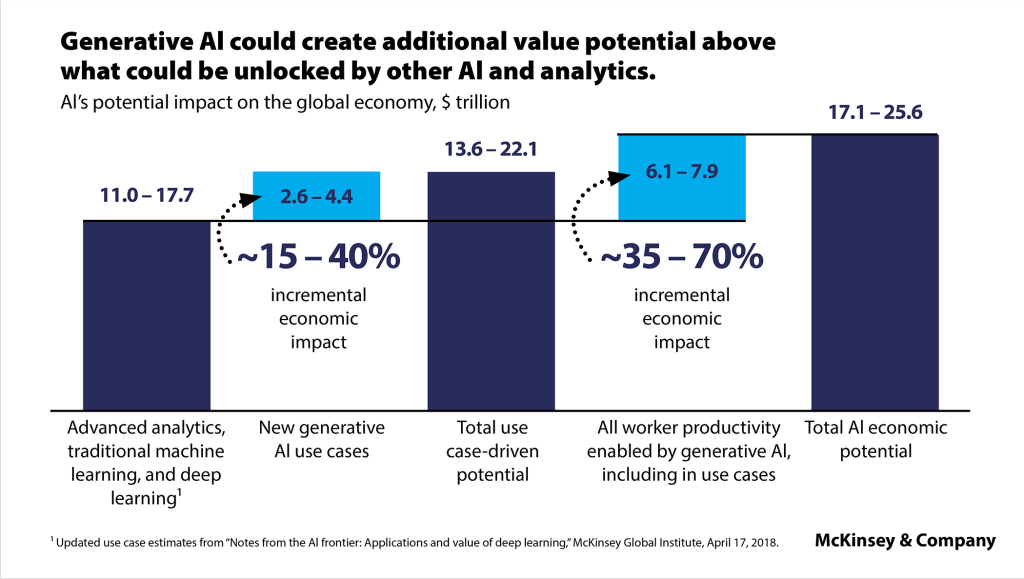
According to a 2023 McKinsey report, Gen AI could add $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy. The US Chamber of Commerce’s Empowering Small Business report (2023 Edition) highlights that 87% of small businesses attribute an increase in efficiency to the use of technology platforms, and 1 in 4 small businesses use AI. Platforms like ChatGPT make AI accessible to small businesses by eliminating the need for large datasets, high computing power, and specialized AI talent. These softwareas-service (SaaS) tools—cloud-based apps—enable SMBs to focus on core business activities while AI handles repetitive tasks, generates insights, and optimizes workflows.
 For small businesses, AI no longer represents just an aspirational goal; it provides a practical solution to enhance growth, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
For small businesses, AI no longer represents just an aspirational goal; it provides a practical solution to enhance growth, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Enhancing Employee Productivity
Small businesses need to provide tools that can augment the productivity of their employees and automate the mundane tasks of their jobs. This allows a team to focus more on their customers and the company’s growth. Some examples of how GenAI can enhance workforce productivity include:
- Content Creation—AI tools like ChatGPT and Claude can generate marketing strategies, draft emails, and refine messaging. Image generation platforms like Midjourney and DALL-E help create compelling visuals, which saves time and enhances creativity. GenAI increases the productivity of the marketing team by not only enabling them to produce a variety of content but also by helping them make quick revisions to their content.
- Data Analysis—Financial analysts spend most of their time analyzing their company’s income statements, balance sheets, spending, and other budgetary issues to gather insights about business performance. Tools like Microsoft CoPilot can simplify data analysis by using natural language prompts to generate insights, summaries, and chart visualizations.
- Document Summarization—Legal teams can save hours using AI-powered tools like Filevine to summarize lengthy documents, extract legal clauses, and highlight key terms without having to comb through the entire document.
Streamlining Business Operations
Small businesses can bring down their operational costs by automating their business processes. Although deterministic systems, where the outcome is fixed and entirely determined by initial parameters, have accomplished some of this automation, they cannot easily handle unstructured data. This is where GenAI tools shine. Some examples include:
- Expense Tracking—Expense management software, such as Yokoy, enables employees to upload their expense receipts and approves them according to company policy. The automated approval process saves accounting staff countless hours of manual review.
- Inventory Management—Several digital tools exist that facilitate inventory management. However, GenAI can augment those tools by tracking inventory in a warehouse through the analysis of images/pictures of pallets, producing inventory lists and streamlining warehouse management.
- Order Management—Most organizations have digitalized their order processing and order fulfillment processes. However, when they need to analyze unstructured data, such as invoice images, they must rely on human intervention. GenAI can reduce this reliance by extracting structured data from invoices to generate reports with details like product lists, quantities, and shipping destinations.
Increasing Customer Engagement
Every business’s priority is to increase its customer lifetime value—the total revenue they expect to receive from a customer over the time they do business together. A business addresses this priority by delighting its patrons and providing them with frictionless experiences. GenAI offers ways to enhance a client’s digital experience by understanding their intent and by simplifying their online shopping journey. Below are a few examples of how to augment customers’ experiences:
- Personalization—Studies show that when brands offer personalized experiences, 80% of consumers more willingly make a purchase. In business-to-business scenarios, GenAI can analyze one business’s transcriptions of conversations between consumers and customer service representatives and then recommend products that the other business can sell to meet the consumers’ needs.
- 24/7 Virtual Assistants—Traditional chatbots help a website’s visitors solely on the basis of predefined logic and cannot make their interactions conversational. GenAI-driven chatbots go further in understanding queries, in directing customers directly to the pertinent content, and even in performing such operations as opening an account or placing an order.
- Sentiment Analysis—Customer feedback mostly exists in textual and visual formats on a company’s website or social media. GenAI can scrape and process this unstructured data to detect customer sentiment and help businesses refine their products and services based on consumer perceptions.
Balancing Opportunities and Risks
While GenAI offers immense potential, small businesses must carefully navigate the associated risks to ensure successful adoption. Common risks and actionable strategies to mitigate them include:
- Proprietary Data Exposure— Proprietary data and business processes represent critical differentiators for SMBs. However, using GenAI tools risks inadvertently sharing sensitive information with GenAI systems or external parties. To mitigate this, employees must learn to use GenAI properly, focusing on safe data handling and appropriate tool usage.
- AI Hallucination—GenAI models are predictive, meaning that they sometimes generate incorrect, misleading, or nonsensical information—referred to as “hallucinations.” Pre-trained models lack knowledge of company-specific data, which increases the risk of irrelevant outputs. To address this problem, employees must validate AI-generated outputs, particularly for critical business decisions.
- Ethical Dilemmas Related to Bias in AI Systems—GenAI systems often inherit societal biases present in training data, which potentially lead to discriminatory outcomes. For instance, a résumé-screening AI system might favor certain demographic groups based on historical hiring patterns. To reduce bias, businesses should engineer prompts by incorporating unbiased examples and should keep a human-in-the-loop (HITL) approach— one that integrates human expertise with AI—within company processes.
- Noncompliance with Regulations—SMBs must adhere to a growing number of data privacy laws, such as GDPR in Europe, HIPAA in US health care, and 19 comprehensive US state privacy laws. Consequences of noncompliance include fines, legal actions, and reputational damage. To ensure compliance, businesses must stay informed about relevant regulations in their industry and region.
- Security Concerns—AI systems can experience cyberattacks, and bad actors may exploit vulnerabilities to access sensitive data or manipulate outputs through prompt injections. To counter these threats, businesses must establish security policies and employ technical guardrails.
Leveraging AI for Growth and Success
Gen AI transforms how small businesses operate, making once-exclusive technologies accessible to all. By leveraging GenAI for workforce productivity, operational efficiency, and customer engagement, small businesses can foster customer loyalty and achieve sustainable growth. However, the benefits of GenAI come with responsibilities. Businesses must address ethical concerns, prioritize data security, and comply with evolving regulations. SMBs should start small by experimenting with GenAI tools tailored to specific needs and then scale up gradually as they gain confidence and expertise.
GenAI does not replace human ingenuity; it represents a powerful complement to our inventiveness. By adopting AI thoughtfully and responsibly, small businesses can harness its potential and thrive in today’s competitive and dynamic business landscape.
Disclaimer: The author is not affiliated with the tools and companies mentioned in this piece. These are examples from my research at the time of writing this article.
 Prabhmeet Kohli is the Founder of Novamorph, a start-up that provides AI and data strategy to empower small and mid-sized businesses, helping them to grow revenue and improve workforce productivity. She has held executive positions at various companies, including Capital One and Northern Trust, where she provided strategy and technology guidance to build data and AI solutions. Kohli has also launched a business analytics platform at start-ups, including TrainSignal, a company now owned by Pluralsight. The Virginia Department of Small Business and Supplier Diversity arranged for her to meet with small companies to educate them about adopting AI. She has experience in data governance, as well as in risk, AI-product, change, and vendor management. Kohli has an MBA in marketing from the John Sperling School of Business and completed a two-year business analytics program at Harvard Business School. She is a member of the HBR Advisory Council and a Certified Information Privacy Professional US (CIPP/US).
Prabhmeet Kohli is the Founder of Novamorph, a start-up that provides AI and data strategy to empower small and mid-sized businesses, helping them to grow revenue and improve workforce productivity. She has held executive positions at various companies, including Capital One and Northern Trust, where she provided strategy and technology guidance to build data and AI solutions. Kohli has also launched a business analytics platform at start-ups, including TrainSignal, a company now owned by Pluralsight. The Virginia Department of Small Business and Supplier Diversity arranged for her to meet with small companies to educate them about adopting AI. She has experience in data governance, as well as in risk, AI-product, change, and vendor management. Kohli has an MBA in marketing from the John Sperling School of Business and completed a two-year business analytics program at Harvard Business School. She is a member of the HBR Advisory Council and a Certified Information Privacy Professional US (CIPP/US).
This article was originally published in AWIS Magazine. Join AWIS to access the full issue of AWIS Magazine and more member benefits.

